Atopic Dermatitis: Clinical Understanding, Treatment Approaches, and Ongoing Research
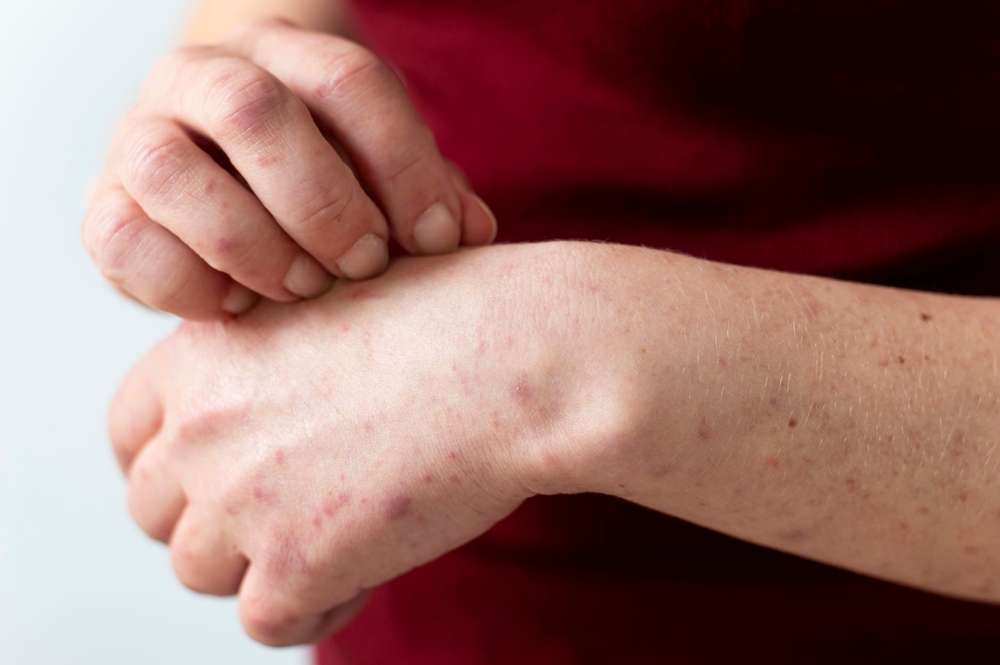
Atopic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition characterized by recurrent flare-ups, itching, and skin barrier dysfunction. It affects both children and adults and may significantly impact quality of life. Advances in dermatological research have expanded treatment options, including topical therapies, systemic medications, and biologic approaches. Understanding the condition requires a long-term, individualized perspective rather than a single solution.

Atopic dermatitis stands as a chronic inflammatory skin disorder characterized by intense itching, red inflamed patches, and compromised skin barrier function. The condition typically manifests in early childhood but can persist into adulthood or develop later in life. Current research indicates that approximately 10-20% of children and 1-3% of adults worldwide experience this condition, making it a significant public health concern requiring comprehensive management approaches.
Dupilumab and Targeted Therapy Developments
Dupilumab represents a breakthrough in targeted therapy for moderate to severe atopic dermatitis. This monoclonal antibody works by blocking interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 signaling pathways, which play crucial roles in the inflammatory cascade associated with atopic dermatitis. Clinical trials have demonstrated significant improvements in disease severity scores and quality of life measures for patients receiving dupilumab treatment. The medication is administered through subcutaneous injection, typically every other week after initial loading doses.
Targeted therapies like dupilumab have transformed treatment approaches by addressing specific molecular mechanisms underlying atopic dermatitis rather than providing broad immunosuppression. This precision allows for more effective symptom control while potentially reducing systemic side effects associated with traditional immunosuppressive medications.
Management Strategies and Treatment Considerations
Addressing atopic dermatitis requires a comprehensive approach combining topical treatments, lifestyle modifications, and systemic therapies when appropriate. Topical corticosteroids remain first-line treatments for acute flares, while topical calcineurin inhibitors offer steroid-sparing alternatives for sensitive areas and long-term maintenance. Moisturizing regimens form the foundation of management, helping restore and maintain skin barrier function.
Systemic treatments become necessary for severe cases unresponsive to topical therapies. Beyond dupilumab, options include traditional immunosuppressants like cyclosporine, methotrexate, and azathioprine. Phototherapy provides another valuable treatment modality, particularly for patients seeking alternatives to systemic medications.
Veterinary Perspectives and Animal Treatment Approaches
Atopic dermatitis also affects companion animals, particularly dogs, where it manifests as canine atopic dermatitis. Veterinary treatment approaches share similarities with human medicine, including topical therapies, allergen avoidance, and systemic medications. Cyclosporine, lokivetmab (a canine-specific monoclonal antibody), and oclacitinib represent important therapeutic options in veterinary dermatology.
Understanding atopic dermatitis in animals provides valuable insights into disease mechanisms and potential therapeutic targets. Comparative studies between human and veterinary medicine continue to inform treatment development across species, highlighting the universal nature of allergic inflammatory processes.
Emerging Therapeutic Developments
Ebglyss represents another advancement in atopic dermatitis treatment, offering patients additional targeted therapy options. This medication targets different inflammatory pathways compared to dupilumab, providing alternatives for patients who may not respond optimally to existing treatments or experience adverse effects.
The development pipeline for atopic dermatitis treatments continues expanding, with researchers investigating novel targets including thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP), interleukin-31, and various kinase inhibitors. These emerging therapies promise to provide more personalized treatment approaches based on individual patient inflammatory profiles.
Research Innovations and Future Directions
Nemluvio and other investigational treatments represent the cutting edge of atopic dermatitis research. These developments focus on understanding the complex interplay between genetic factors, environmental triggers, and immune system dysfunction that characterizes the condition. Biomarker research aims to identify predictive factors that could guide treatment selection and improve patient outcomes.
Current research priorities include developing treatments for pediatric populations, investigating combination therapies, and exploring preventive strategies for high-risk individuals. Microbiome research has revealed important connections between skin bacterial communities and disease severity, opening new avenues for therapeutic intervention.
| Treatment Category | Examples | Mechanism of Action | Typical Cost Range |
|---|---|---|---|
| Topical Corticosteroids | Triamcinolone, Clobetasol | Anti-inflammatory | $20-150/month |
| Topical Calcineurin Inhibitors | Tacrolimus, Pimecrolimus | Immune modulation | $200-400/month |
| Targeted Biologics | Dupilumab, Tralokinumab | Cytokine blocking | $3,000-4,500/month |
| JAK Inhibitors | Upadacitinib, Abrocitinib | Kinase inhibition | $3,500-4,000/month |
| Traditional Immunosuppressants | Cyclosporine, Methotrexate | Broad immunosuppression | $50-300/month |
Prices, rates, or cost estimates mentioned in this article are based on the latest available information but may change over time. Independent research is advised before making financial decisions.
This article is for informational purposes only and should not be considered medical advice. Please consult a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance and treatment.
The landscape of atopic dermatitis treatment continues evolving rapidly, with new therapeutic options providing hope for patients with previously treatment-resistant disease. As research advances our understanding of disease mechanisms, treatment approaches become increasingly sophisticated and personalized. The integration of traditional therapies with novel targeted treatments offers comprehensive management strategies that can significantly improve patient quality of life and long-term outcomes.